
英语原文共 11 页,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
外文原文:
Assessing the performance of microfinance lending process using AHP-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method: Moroccan case study
Youssef Lamrani Alaoui and Mohamed Tkiouat
Abstract
Many studies focus on microfinance institutions (MFIs) profitability, client retention, and default rate. Yet, they do not pay much attention to the way in which microfinance (MF) can improve the living conditions of the poor and satisfy their needs. This article presents a new way to assess the performance of MF lending process based on analytic hierarchy process (AHP)-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. The aim is to suggest some solutions to improve the performance of processes that create and support MF products and services. Not only should this study contribute to the research literature but it can also help the MFIs to control the risk derived from their operations and increase client satisfaction. Thus, MFIs can enhance their performance and their role in reducing poverty.
Keywords
Microfinance lending process, AHP, Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method
Introduction
Microfinance is a set of financial services designed to serve the unbanked poor.1 The financial service needs of poor people are diverse and complex which represent opportunities that can be met on a profitable basis.2 Poor people need access to financial services to reduce their vulnerability, to meet anticipated and unanticipated needs, and to take advantage of opportunities as they arise. To do so, microfinance institutions (MFIs) provide a web of different financial products like saving services, microcredit, insurance, payment services,3 and even micropensions.4 MFIs may also include different activities like skill training and entrepreneurial education directly or in partnership with other institutions. However, the majority of academics and practitioners focus neither on customersrsquo; needs nor in the ways to improve their lives. Rather than that, studies are based on MFIs perception, that is, profitability, client retention, default rates, and the number of customers as the primary measures.5,6 Kanyurhi7 notes that the MFIrsquo;s weakness to satisfy their clientsrsquo; needs is one of the main reasons they lose customers.
Customer satisfaction results in designing appropriate products and services and in the efficiency and effectiveness of the processes creating them. Improving MF processes can help the MFIs achieving such objectives and manage the risks derived from their operations.8 Several processes such as lending process, saving management process, and payments management process characterize the MFIsrsquo; operations. However, the loan process represents the most typical one.
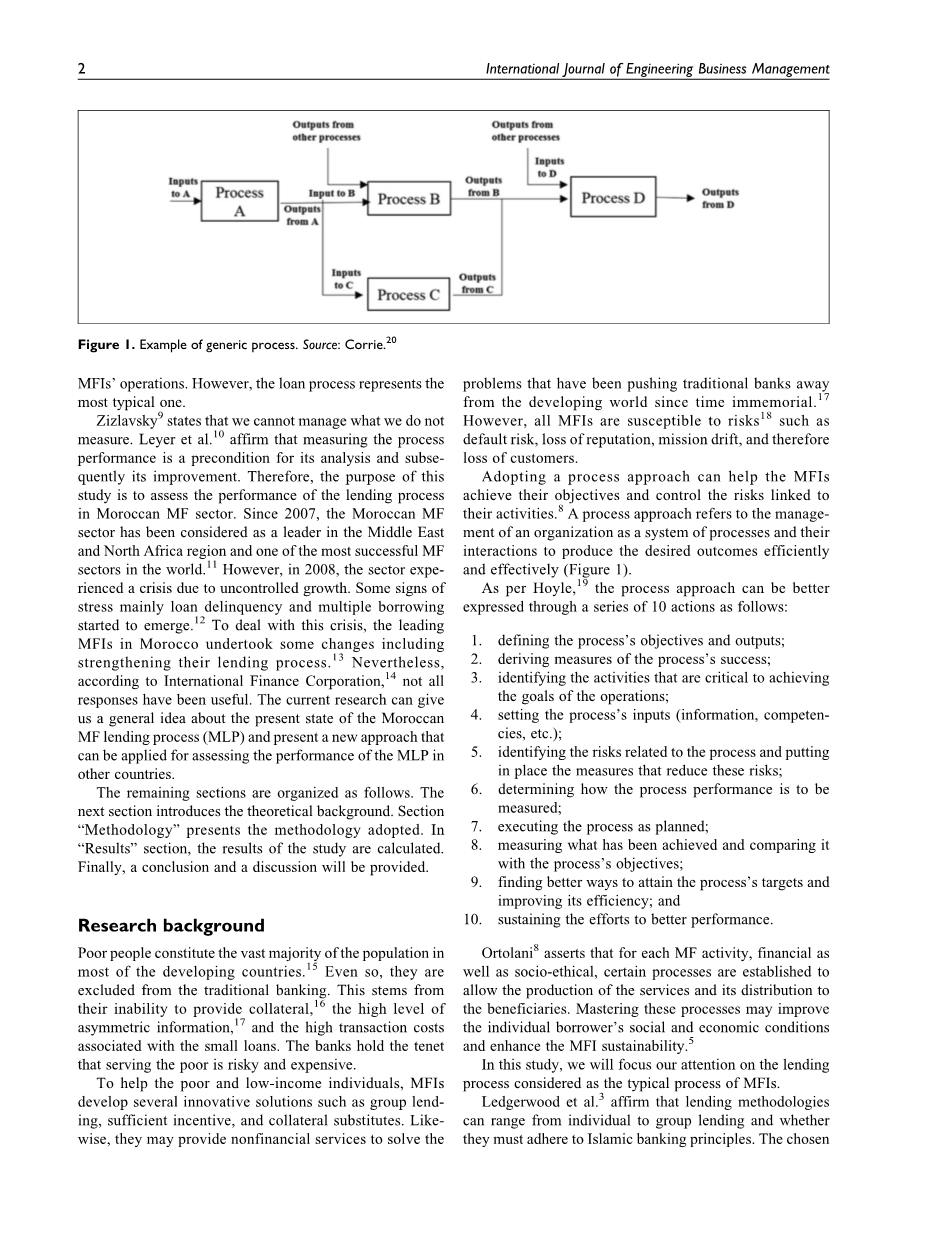
Figure 1. Example of generic process. Source: Corrie.20
Zizlavsky9 states that we cannot manage what we do not measure. Leyer et al.10 affirm that measuring the process performance is a precondition for its analysis and subsequently its improvement. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to assess the performance of the lending process in Moroccan MF sector. Since 2007, the Moroccan MF sector has been considered as a leader in the Middle East and North Africa region and one of the most successful MF sectors in the world.11 However, in 2008, the sector experienced a crisis due to uncontrolled growth. Some signs of stress mainly loan delinquency and multiple borrowing started to emerge.12 To deal with this crisis, the leading MFIs in Morocco undertook some changes including strengthening their lending process.13 Nevertheless, according to International Finance Corporation,14 not all responses have been useful. The current research can give us a general idea about the present state of the Moroccan MF lending process (MLP) and present a new approach that can be applied for assessing the performance of the MLP in other countries.
The remaining sections are organized as follows. The next section introduces the theoretical background. Section “Methodology” presents the methodology adopted. In “Results” section, the results of the study are calculated. Finally, a conclusion and a discussion will be provided.
Research background
Poor people constitute the vast majority of the population in most of the developing countries.15 Even so, they are excluded from the traditional banking. This stems from their inability to provide collateral,16 the high level of asymmetric information,17 and the high transaction costs associated with the small loans. The banks hold the tenet that serving the poor is risky and expensive.
To help the poor and low-income individuals, MFIs develop several innovative solutions such as group lending, sufficient incentive, and collateral substitutes. Likewise, they may provide nonfinancial services to solve the problems that have been pushing traditional banks away from the developing world since time immemorial.17 However, all MFIs are susceptible to risks 18 such as default risk, loss of reputation, mission drift, and therefore loss of customers.
Adopting a process approach can help the MFIs achieve their objectives and control the risks linked to their activities.8
剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
资料编号:[237365],资料为PDF文档或Word文档,PDF文档可免费转换为Word


