
英语原文共 18 页,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
Copper-boryl mediated organic synthesis
Organoboron compounds are valuable synthetic intermediates that find application in a diverse variety of processes including both C–X and C–C bond-forming transformations. This has been achieved by using a variety of boron derivatives. Of these, boronate esters are probably the most versatile and, reflecting this, methods for the generation of boronate esters are of considerable current interest. Given the mild reaction conditions, good functional group tolerance, and low cost of the metal catalyst, the use of copper-boryl reagents is particularly attractive. In this review, methodologies in copper-boryl chemistry are discussed and the many different transformations possible are surveyed.
1 Organoboron compounds
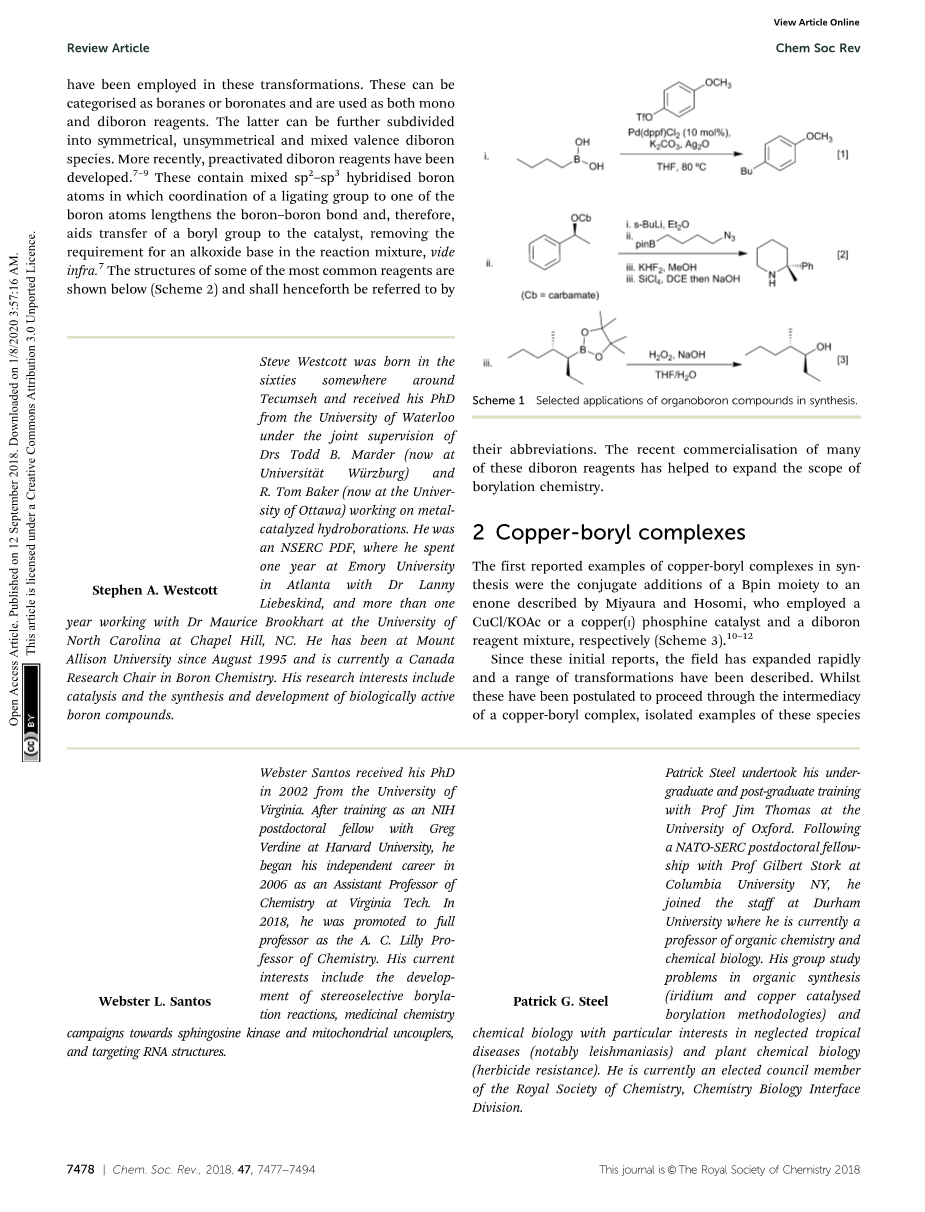
Organoboron compounds are highly important synthetic intermediates that find application in a diverse variety of synthetic processes including both C–X and C–C bond forming transformations exemplified by the Suzuki–Miyaura cross coupling and 1,2-metallate rearrangements including aminations and oxidation reactions (Scheme 1).1–3
These have employed a variety of boron derivatives including alkyl, vinyl and aryl boranes, boronate esters and related compounds. Of these, the boronate esters are probably the most versatile being non-toxic, tolerant to air and water, whilst reacting under relatively mild conditions to produce an inert, benign and easy to separate by-product. Reflecting this, methods for the generation of boronate esters are of considerable current interest. Classically, this is achieved via the reaction of hard organometallic reagents with borate esters or through hydroboration strategies. Such methods, however, have relatively limited substrate scope and, more recently, milder catalysed C–H and C–X borylation strategies have emerged.4–6 Of these, processes mediated by a copper-boryl species are particularly prominent enabled by mild reaction conditions, good functional group tolerance, and low cost of the metal catalyst. In this review, developments in this area are surveyed. Space precludes a comprehensive discussion and we have attempted to focus on aspects that best illustrate the many different possibilities enabled by using these reagents in synthesis.
1.1 Boron reagents
In parallel with the breadth of chemistry possible using copperboryl reagents, there is a diverse range of boron reagents thathave been employed in these transformations. These can be categorised as boranes or boronates and are used as both mono and diboron reagents. The latter can be further subdivided into symmetrical, unsymmetrical and mixed valence diboron species. More recently, preactivated diboron reagents have been developed.7–9These contain mixed sp2–sp3hybridised boron atoms in which coordination of a ligating group to one of the boron atoms lengthens the boron–boron bond and, therefore, aids transfer of a boryl group to the catalyst, removing the requirement for an alkoxide base in the reaction mixture, vide infra.7 The structures of some of the most common reagents are shown below (Scheme 2) and shall henceforth be referred to bytheir abbreviations. The recent commercialisation of many of these diboron reagents has helped to expand the scope of borylation chemistry.
2 Copper-boryl complexes
The first reported examples of copper-boryl complexes in synthesis were the conjugate additions of a Bpin moiety to an enone described by Miyaura and Hosomi, who employed a CuCl/KOAc or a copper(I) phosphine catalyst and a diboron reagent mixture, respectively (Scheme 3).10–12
Since these initial reports, the field has expanded rapidly and a range of transformations have been described. Whilst these have been postulated to proceed through the intermediacy of a copper-boryl complex, isolated examples of these species are relatively rare. Predominantly, it is for NHC bound copperboryls that molecular structures have been reported although a very recent report describes phosphine bound complexes.13–17 For most NHC complexes, a linear arrangement, with the Bpin moiety bound directly opposite to the NHC ligand, was observed (Scheme 4). DFT and in situ11B NMR studies also provide some insight into their formation, with the11B NMR signal for a copper bound boryl moiety observed atd = 4 2 p p m .18–21 It has been calculated that the Cu–B s* molecular orbital is high in energy, with the filled Cu–B s-bond being more likely to interact with the substrate consistent with the model of a nucleophilic boron reagent.22However, the recent studies by Kleeburg suggest that whilst monomeric copper-boryl species cannot be excluded such analysis does require the consideration of higher aggregates which challenge classical mechanistic interpretations.
Accepting this reservation, in the majority of borylation reactions, the active catalysts are generally formed in situ by the reaction of a copper(I) salt with an alkoxide base.23 A metathesis reaction with the diboron reagent then occurs, generating the active copper-boryl complex. Coordination of the substrate and insertion (Scheme 5, shown with an alkene) then occurs, affording a new borylorganocopper intermediate. Following reaction with an electrophile, ligand exchange with the alkoxide base regenerates the copper alkoxide complex.
3 Synthetic transformations mediated by copper-boryl complexes
The mode of reaction of the copper-boryl complex is largely defined by the nature of the substrate structure and this review is organised along these lines, focussing on issues of chemo-, regio- and stereoselectivity. This has been achieved using a diverse range of ligands, with phosphines and NHCs being the most commonly employed. As indicated above, the ultimate boron containing product is readily converted into a range offunctional groups and this review will focus on the steps involved in the formation of the organoboron intermediate an
剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
资料编号:[236767],资料为PDF文档或Word文档,PDF文档可免费转换为Word
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 通过对奥美拉唑合成反应的监测和定量反应的在线拉曼光谱和表征组件外文翻译资料
- 无金属碳基催化剂的研究进展外文翻译资料
- 钼酸钙/碳三维复合材料可控设计合成的研究外文翻译资料
- 生物催化选择性合成功能化喹唑啉酮衍生物外文翻译资料
- 三元V Zr Al ON氧氮化物-3-甲基吡啶氨氧化的高效催化剂外文翻译资料
- 综述纳米零价铁(nZVI)的合成,特性和在环境修复中的应用外文翻译资料
- 自消毒PVC表面使用点击化学设计外文翻译资料
- 微波辅助直接合成4H-1,2,4-苯并噻二嗪1,1-二氧化物衍生品外文翻译资料
- 微波辅助下直接合成1,1-二氧代-4H-1,2,4-苯并噻二嗪类衍生物外文翻译资料
- 压力选择在变压精馏中的重要性外文翻译资料


